Spring Reactive는 비동기적이고 논블로킹(Non-blocking) 방식으로 데이터를 처리하는 방법을 제공하는 Spring의 기능입니다. 주로 Spring
WebFlux라는 모듈을 통해 구현되며, 이는 서버 응답의 지연 시간을 줄이고 높은 동시성을 처리할 수 있도록 돕습니다.
비동기처리
@GetMapping("rest")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<String>> rest(@RequestParam int idx) {
String url = "/service?req={req}";
// 첫 번째 요청 보내기
return webClient.get()
.uri(url, "rest" + idx)
.retrieve()
.toEntity(String.class)
.flatMap(response -> {
// 첫 번째 요청이 성공하면, 두 번째 비동기 요청 처리
String res = response.getBody();
log.debug("First request succeeded: " + res);
// 두 번째 서버와의 비동기 요청
return sendSecondRequest(response.getBody())
.flatMap(secondResponse -> {
// @Async 메서드 호출하여 비동기로 combinedResponse 생성
return Mono.fromFuture(innerService.createCombinedResponseAsync(response.getBody(),
secondResponse.getBody()));
})
.map(combinedResponse -> ResponseEntity.ok(combinedResponse));
})
.doOnTerminate(() -> {
// 첫 번째 요청이 완료되면 실행
log.debug("First request completed!");
})
.doOnError(error -> {
// 첫 번째 요청이 실패하면 처리
log.debug("First request failed: " + error.getMessage());
});
}
InnerService
@EnableAsync
public static class InnerService {
@Async(value = "tp")
public CompletableFuture<String> createCombinedResponseAsync(String firstResponse, String secondResponse) {
log.debug("call createCombinedResponseAsync.... on thread: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
String combinedResponse = "ASYNC WORK >> " + firstResponse + " |||| " + secondResponse;
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(combinedResponse);
}
}
Thread Pool
@Bean
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor tp() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor te = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
te.setCorePoolSize(1); //첫 요청이 들어오면 10개의 쓰레드를 만들어둠
te.setMaxPoolSize(1); // queue가 꽉차면 추가적으로 늘어나는 쓰레드 수 즉, 최대쓰레드 200 + 100
//te.setQueueCapacity(200);
te.setThreadNamePrefix("Woo-Thread");
te.initialize();
return te;
}
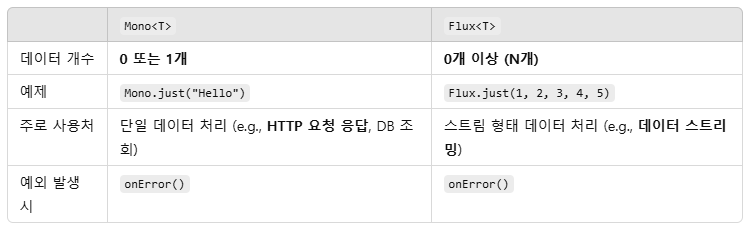
Mono, Flux
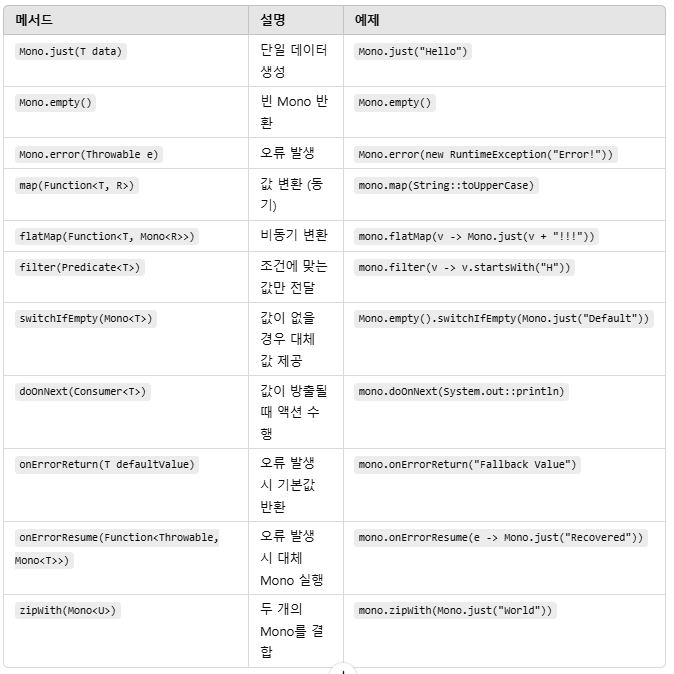
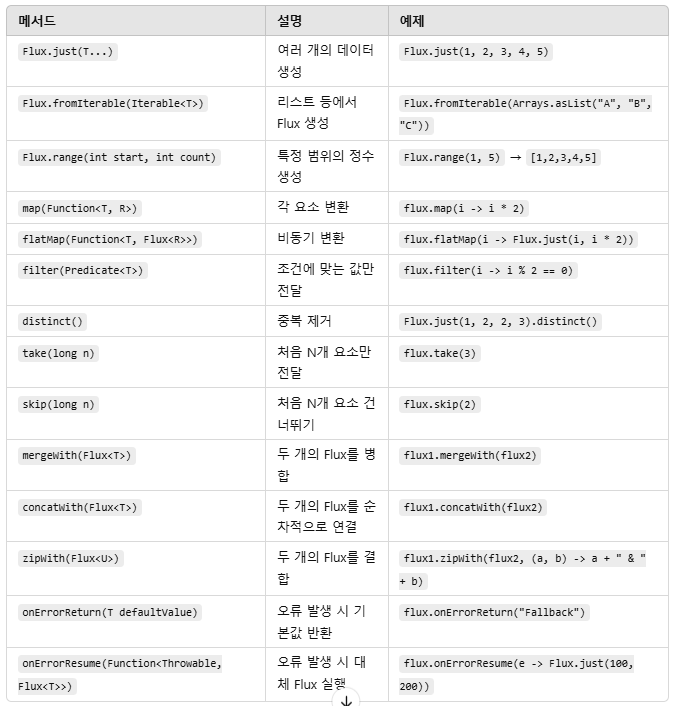
`Mono<T>`와 `Flux<T>`는 Spring WebFlux에서 리액티브 스트림을 다룰 때 사용되는 기본적인 타입이며, 다양한 연산자를 제공합니다
`Mono`의 주요메소드
`Flux`의 주요메소드
package com.exam.react2;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import reactor.core.publisher.Mono;
@SpringBootApplication
@RestController
@Slf4j
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unchecked"})
public class React2Application {
@GetMapping("/")
Mono<String> hello() {
log.debug("call hello()... start");
Mono mono = Mono.just("Hello WebFlux").doOnNext(c->log.debug(c)).log();
log.debug("call hell()... end");
//log() : publisher
//만들어둔 Mono는 스프링에서 subscribe하면서 실행됨
return mono;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(React2Application.class, args);
}
}
Mono 선언 및 체이닝:이 부분에서는 Mono가 정의될 뿐, 실제로 실행되지는 않습니다.
Mono는 "Hello WebFlux"라는 데이터를 생성하고, .doOnNext와 .log() 연산자를 추가하여 처리 흐름을 준비하지만, 데이터 생성 및 처리 실행은 구독(Subscription)이 발생할 때 실행됩니다.
`return mono`: 컨트롤러 또는 다른 메서드에서 반환된 Mono는 구독자(Spring)가 생길 때 실행됩니다.
즉, 쓰레드에서
`log.debug("call hello()... start");`
`log.debug("call hell()... end");`
이 먼저 수행되고
`Mono mono = Mono.just("Hello WebFlux").doOnNext(c->log.debug(c)).log();`
는 별도의 쓰레드에서 수행됩니다.
1. map()
- 역할: 각 데이터를 변환합니다.
- 입력과 출력: 입력 데이터를 변환하여 새로운 값 또는 객체를 반환합니다. 반환 값은 Mono 또는 Flux가 아니라 일반 값입니다.
- 비동기 작업에 적합하지 않음: map()은 동기적으로 데이터를 변환하며, 비동기 작업을 처리하지 않습니다.
webClient.get()
.uri("/example")
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.map(response -> "Modified: " + response) // 동기적 데이터 변환
.subscribe(System.out::println);설명:
- /example의 응답 데이터를 받아 "Modified: " + response로 변환.
2. flatMap()
- 역할: 데이터를 변환하여 새로운 Mono 또는 Flux를 반환합니다.
- 입력과 출력: 입력 데이터를 변환하고, 변환 결과를 비동기적으로 처리할 수 있는 Mono 또는 Flux로 반환합니다.
- 비동기 작업에 적합: flatMap()은 비동기 작업에서 다른 서비스 호출이나 추가 비동기 작업을 연결할 때 사용됩니다.
webClient.get()
.uri("/example")
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.flatMap(response -> webClient.post() // 비동기 작업 연결
.uri("/process")
.bodyValue(response)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class))
.subscribe(System.out::println);설명:
- /example의 응답 데이터를 받아 /process로 POST 요청을 보냄.
- flatMap()을 통해 응답 데이터를 비동기적으로 연결.
DeferredResult
Spring의 DeferredResult 큐는 비동기 요청 처리에서 주로 사용되며, 서버가 비동기적으로 처리해야 하는 요청을 잠시 기다렸다가 이후에 응답할 수 있도록 만들어주는 기술입니다. DeferredResult는 Spring MVC에서 비동기 요청을 처리하기 위해 제공하는 클래스로, 요청의 결과가 준비될 때까지 클라이언트 연결을 유지하면서도 서블릿 컨테이너의 스레드를 차지하지 않게 합니다.
DeferredResult의 동작 방식
- 요청 큐에 넣기: 클라이언트가 HTTP 요청을 보내면 컨트롤러는 해당 요청을 처리하기 위해 DeferredResult 객체를 반환하고, 이 요청을 큐에 저장합니다. DeferredResult는 아직 완료되지 않은 상태입니다.
- 비동기 작업 수행: 요청을 바로 처리하지 않고, 별도의 비동기 작업(예: 스레드, 스레드 풀, 메시지 큐)을 통해 응답을 준비합니다. 예를 들어, 오래 걸리는 백그라운드 작업이 완료될 때까지 요청을 대기시킵니다.
- 결과 반환: 비동기 작업이 완료되면 DeferredResult 객체에 값을 설정하여 응답을 준비하고, 이를 통해 클라이언트에 응답을 보냅니다.
Queue<DeferredResult<String>> q = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
@GetMapping("/dr")
public DeferredResult<String> deferredResult() {
log.info("call DeferredResult() ...");
DeferredResult<String> dr = new DeferredResult<>(600000L);
q.add(dr);
return dr;
}
@GetMapping("/dr/count")
public String drCount() {
return String.valueOf(q.size());
}
@GetMapping("/dr/event")
public String drEvent(String msg) {
for(DeferredResult<String> dr : q) {
dr.setResult("Hello " + msg);
q.remove(dr);
}
return "SUCCESS";
}
WebClient
Spring WebClient는 Spring 5에서 도입된 비동기 및 반응형 웹 클라이언트로, HTTP 요청을 수행하고 응답을 처리하는 데 사용됩니다. WebClient는 반응형 프로그래밍을 지원하여 비동기 방식으로 HTTP 요청을 쉽게 수행할 수 있도록 도와줍니다.
주요 특징
- 비동기 요청 처리: 요청을 보내고 응답을 기다리는 동안 다른 작업을 계속할 수 있습니다.
- 반응형 스트림 지원: Publisher와 Subscriber의 개념을 사용하여 데이터 흐름을 제어합니다.
- 유연한 API: 다양한 HTTP 메서드(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 등)를 지원하며, 요청과 응답을 쉽게 구성할 수 있습니다.
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
@Component
public class WebClientExample implements CommandLineRunner {
private final WebClient webClient;
public WebClientExample(WebClient.Builder webClientBuilder) {
this.webClient = webClientBuilder.baseUrl("https://api.example.com").build();
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// GET 요청
webClient.get()
.uri("/endpoint")
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.subscribe(response -> System.out.println("GET Response: " + response));
// POST 요청
MyRequestObject requestObject = new MyRequestObject("example data");
webClient.post()
.uri("/endpoint")
.bodyValue(requestObject)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(MyResponseObject.class)
.subscribe(response -> System.out.println("POST Response: " + response));
}
}
Future
Java의 Future 인터페이스는 비동기 작업의 결과를 나타내는 객체입니다. 이를 통해 현재 실행 중인 작업의 완료 상태를 비동기적으로 확인하거나 결과를 가져올 수 있습니다. 주로 Java의 멀티스레드나 비동기 작업에서 사용되며, 특히 ExecutorService에서 반환되는 submit() 메서드의 반환 타입으로 많이 활용됩니다.
주요 메서드
- get(): 작업이 완료될 때까지 기다렸다가 결과를 반환합니다. 만약 작업이 완료되지 않으면 블로킹 상태가 되어 기다리게 됩니다. 예외 발생 시 ExecutionException이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit): 특정 시간 동안만 기다리고, 해당 시간 내에 작업이 완료되지 않으면 TimeoutException을 발생시킵니다.
- cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning): 작업을 취소할 수 있습니다. 작업이 시작되지 않았거나 아직 완료되지 않았다면 취소할 수 있고, 작업이 취소되면 isCancelled() 메서드가 true를 반환합니다.
- isDone(): 작업이 완료되었는지 확인합니다. 완료되었으면 true를 반환합니다.
- isCancelled(): 작업이 취소되었는지 확인합니다. 취소되었으면 true를 반환합니다.
예제 코드
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class FutureExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 비동기 작업 제출
Future<Integer> future = executor.submit(() -> {
Thread.sleep(2000); // 작업 시뮬레이션 (2초 대기)
return 42;
});
try {
System.out.println("작업 결과 대기 중...");
Integer result = future.get(); // 결과가 준비될 때까지 기다림
System.out.println("작업 결과: " + result);
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
executor.shutdown();
}
}
}
Sprint Reactive 참고
'WEB개발 > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] Request를 처리하는 주석 (Annotation) (0) | 2025.02.21 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] Spring Security (0) | 2024.08.23 |
| 하이버네이트(Hibernate) & JPA(Java Persistence API) (0) | 2024.05.23 |
| [SpringBoot] 스프링부트 오류모음 (0) | 2024.03.27 |
| [SPRING]DI (MAP, SET, LIST), Root Application Context, Servlet Application Context (0) | 2023.03.07 |



